November is Diabetes Awareness Month
Did you know that diabetic retinopathy is the current leading cause of blindness in adults in the U.S.? The condition is serious, but the fortunate news for patients is that with proper screening, a majority of devastating vision loss is preventable. We encourage patients with diabetes to make regular annual visits to an eye care professional a priority, particularly as they age. Spending an hour or less at your doctor’s office once a year could mean the difference between potentially losing all vision and effective treatment that prevents such a loss.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that occurs in the retina that generally results from chronically elevated blood glucose levels. Glycosylation of these blood vessels can lead to breakdown of blood vessel walls, leakage and swelling and ultimately decreased vision. In addition, unstable new blood vessels can form that can break and bleed, which can also lead to decreased vision.
Diabetic retinopathy, although the leading cause of blindness in patients under the age of 55 in the US, is largely preventable with proper screening and treatment.
How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
Up to 60% of diabetic patients are not properly screened for diabetic retinopathy. Proper screening can consist of yearly visits to an eye care professional or, more recently, telemedicine screening visits in a primary care setting. Through local telemedicine partnerships, Austin Retina is pleased to have seen up to 80% compliance rates, ultimately saving the sight of thousands.
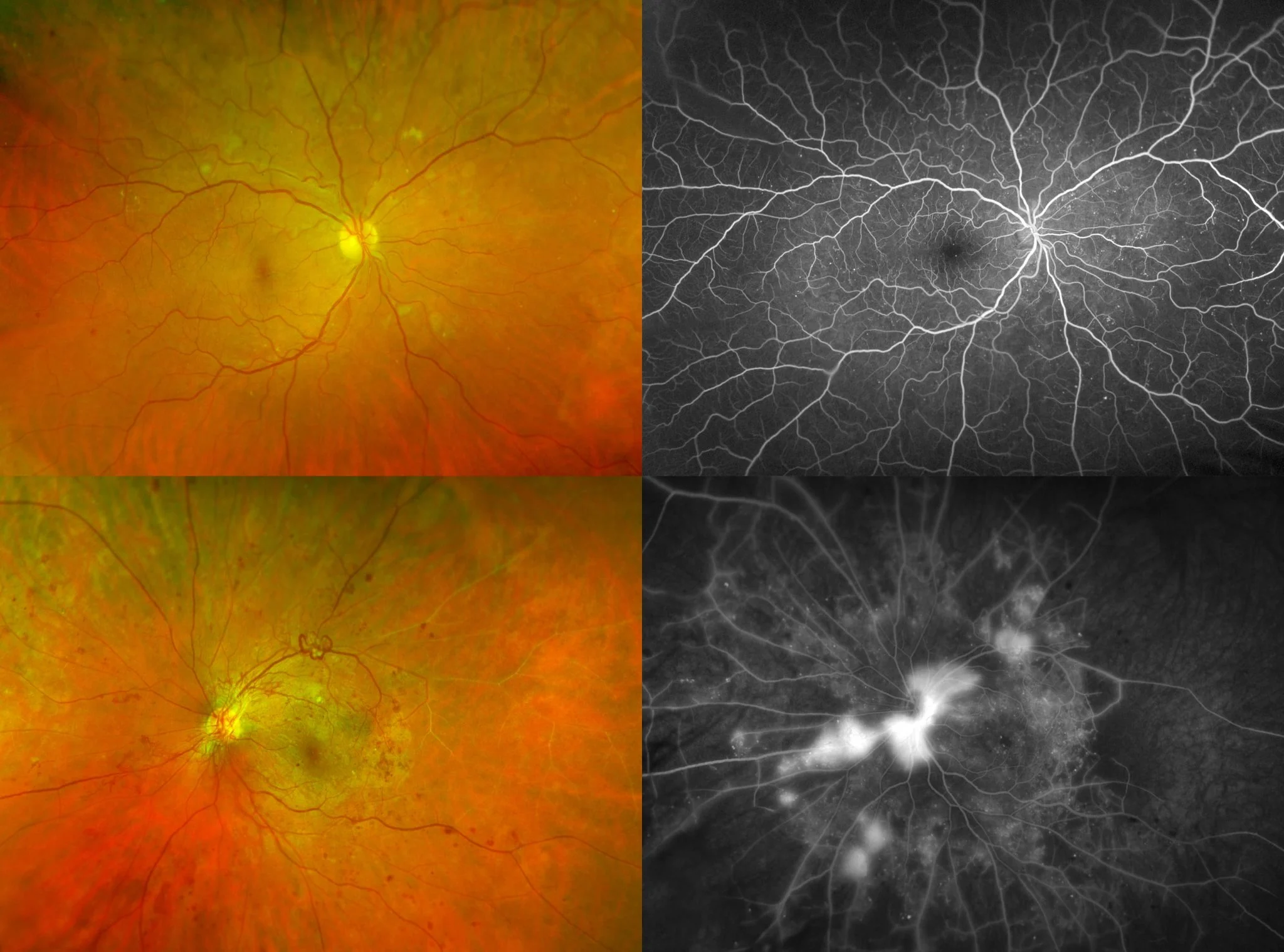
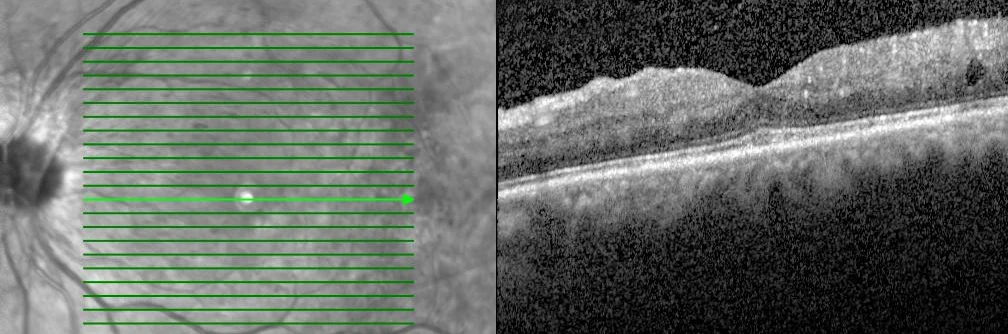
Once any diabetic retinopathy is detected on initial screening, other testing modalities such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiogram imaging are employed. OCT is an excellent tool used to detect subtle changes in macular thickness, which often occurs in early diabetic maculopathy. Optos fluorescein angiogram wide-angle imaging is critical in analyzing the peripheral retina for ischemia and neovascularization, both of which can be easily missed by direct examination or routine photography.
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
The two critical variables for control of diabetic retinopathy are blood pressure and blood glucose.
Controlling blood glucose (hemoglobin A1C less than 7%) limits the destruction that can occur from glycosylation of small blood vessels in the retina. In most cases, this can be achieved through diet and exercise. Controlling blood pressure decreases the amount of leakage and swelling that can occur from these already damaged blood vessels.
The newest treatments for diabetic retinopathy involve the use of medications that can be effective not only in stabilizing the condition but also in restoring vision. These medications are injected into the eye through an office-based procedure called an intravitreal injection. This relatively painless injection through the white part of the eye is performed after the eye is thoroughly anesthetized with topical eye drops. Additionally, medications such as Eylea, Lucentis, and Avastin have the potential to improve vision by reducing the amount of macular edema caused by diabetic retinopathy.
Do you have questions? Please contact Austin Retina directly so we can assist. You can request an appointment online here or call our office at 800-252-8259 during normal business hours.